Corrosion Electrochemical Analysis Cell (May 2024 - August 2024)
This research project was presented at the USF Summer Research Sympossioum. Poster is bellow.


Purpose
The cell apparatus was designed with the intent of analyzing corrosion activity at small spots along a corroded region in a steel reinforcement. It is believed that in some cases the corroded regions may naturally go through repassivation, further protecting the reinforcement from further corrosion damage.
Design
To favor rapid prototyping and design iterations, the cell was printed using additive manufacturing technologies. The cell was printed using Stereolithography (SLA). The housing assembly was printed using standard Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). The mechanical design was made in SolidWorks. The design of testing apparatus was focused on being reliable, inexpensive and easy to expand on.
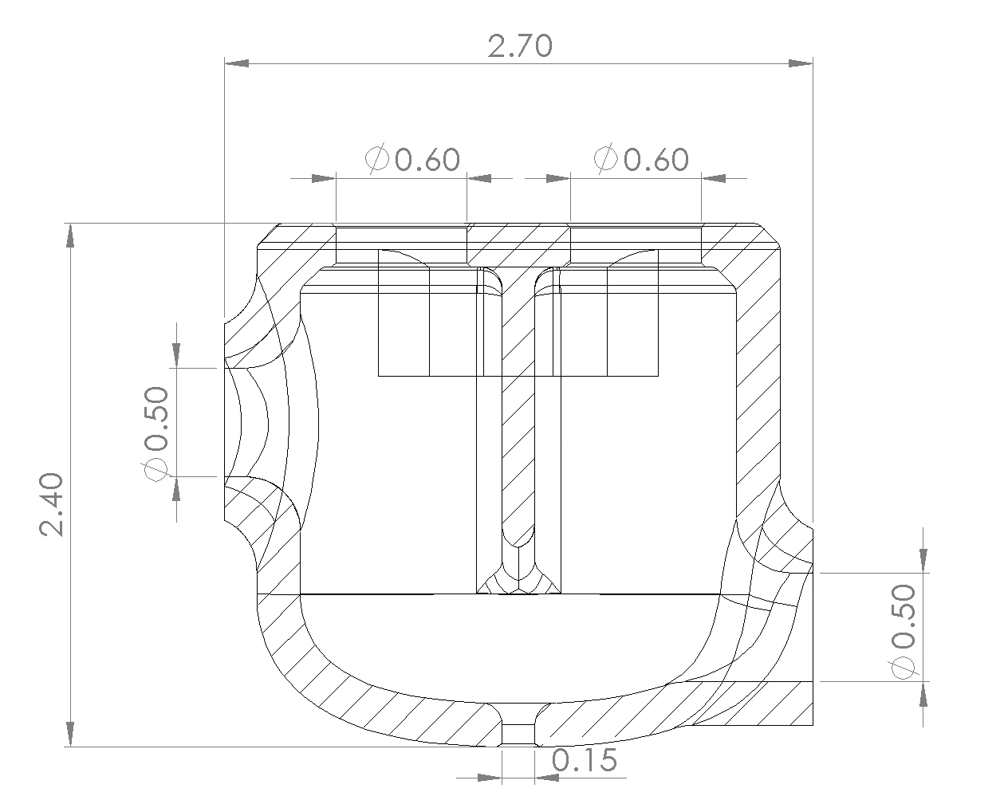
- Separation of the CE and RE
- Opening area of 2.25 mm^2
- Electrolyte volume of 5.4 mL
- Sealing Silicone – mitigate electrolyte leaking
- Lead Screw – clamping force on sample
- Housing Assembly – fix the cell on area of interest
Simulation
To predict the behavior of the cell and validate the design, COMSOL Multiphysics simulation packages were used. A concentrated current density along the center of the opening was desired, meaning that measurements would be localized. The geometry of the cell was imported into the software, and then a simulation was done under the expected testing conditions. The results indicated a concentrated current density between the electrolytes and the testing sample.
